Advantages of Graviton Processor Instances for Your Workloads
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) Graviton2 processor-based instances utilizing 64-bit Arm Neoverse cores.
AWS Graviton2 processors deliver a significant leap in performance and capabilities over the first-generation AWS Graviton processor (A1 series) instances. Amazon boasts that these new instances provide up to a 40% better price and performance over comparable current generation x86-based instances for a wide variety of workloads.
Amazon has released Graviton2 instances across General Purpose, Compute Optimized, and Memory Optimized families in M6g, C6g, and R6g types. For applications that require local storage, NVMe SSD local instance storage variants like C6gd, M6gd, and R6gd are available.
| Instance Size | vCPUs | Memory (GiB) | Instance Storage (GIB) | Network Bandwidth (Gbps) | EBS Bandwidth (Mbps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6g.medium | 1 | 4 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| m6g.large | 2 | 8 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| m6g.xlarge | 4 | 16 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| m6g.2xlarge | 8 | 32 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| m6g.4xlarge | 16 | 64 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | 4,750 |
| m6g.8xlarge | 32 | 128 | EBS-only | 12 | 9,000 |
| m6g.12xlarge | 48 | 192 | EBS-only | 20 | 13,500 |
| m6g.16xlarge | 64 | 256 | EBS-only | 25 | 19,000 |
| m6g.metal | 64 | 256 | EBS-only | 25 | 19,000 |
| m6gd.medium | 1 | 4 | 1×59 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| m6gd.large | 2 | 8 | 1×118 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| m6gd.xlarge | 4 | 16 | 1×237 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| m6gd.2xlarge | 8 | 32 | 1×474 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| m6gd.4xlarge | 16 | 64 | 1×950 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | 4,750 |
| m6gd.8xlarge | 32 | 128 | 1×1900 NVMe SSD | 12 | 9,000 |
| m6gd.12xlarge | 48 | 192 | 2×1425 NVMe SSD | 20 | 13,500 |
| m6gd.16xlarge | 64 | 256 | 2×1900 NVMe SSD | 25 | 19,000 |
| m6gd.metal | 64 | 256 | 2×1900 NVMe SSD | 25 | 19,000 |
| Instance Size | vCPUs | Memory (GiB) | Instance Storage (GiB) | Network Bandwidth (Gbps) | EBS Bandwidth (Mbps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c6g.medium | 1 | 2 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| c6g.large | 2 | 4 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| c6g.xlarge | 4 | 8 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| c6g.2xlarge | 8 | 16 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| c6g.4xlarge | 16 | 32 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | 4750 |
| c6g.8xlarge | 32 | 64 | EBS-only | 12 | 9000 |
| c6g.12xlarge | 48 | 96 | EBS-only | 20 | 13500 |
| c6g.16xlarge | 64 | 128 | EBS-only | 25 | 19000 |
| c6g.metal | 64 | 128 | EBS-only | 25 | 19000 |
| c6gd.medium | 1 | 2 | 1×59 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| c6gd.large | 2 | 4 | 1×118 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| c6gd.xlarge | 4 | 8 | 1×237 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| c6gd.2xlarge | 8 | 16 | 1×474 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| c6gd.4xlarge | 16 | 32 | 1×950 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | 4,750 |
| c6gd.8xlarge | 32 | 64 | 1×1900 NVMe SSD | 12 | 9,000 |
| c6gd.12xlarge | 48 | 96 | 2×1425 NVMe SSD | 20 | 13,500 |
| c6gd.16xlarge | 64 | 128 | 2×1900 NVMe SSD | 25 | 19,000 |
| c6gd.metal | 64 | 128 | 2×1900 NVMe SSD | 25 | 19,000 |
| Instance Size | vCPUs | Memory (GiB) | Instance Storage | Network Bandwidth (Gbps) | EBS Bandwidth (Mbps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r6g.medium | 1 | 8 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| r6g.large | 2 | 16 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| r6g.xlarge | 4 | 32 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| r6g.2xlarge | 8 | 64 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| r6g.4xlarge | 16 | 128 | EBS-only | Up to 10 | 4750 |
| r6g.8xlarge | 32 | 256 | EBS-only | 12 | 9000 |
| r6g.12xlarge | 48 | 384 | EBS-only | 20 | 13500 |
| r6g.16xlarge | 64 | 512 | EBS-only | 25 | 19000 |
| r6g.metal | 64 | 512 | EBS-only | 25 | 19000 |
| r6gd.medium | 1 | 8 | 1×59 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| r6gd.large | 2 | 16 | 1×118 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| r6gd.xlarge | 4 | 32 | 1×237 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| r6gd.2xlarge | 8 | 64 | 1×474 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | Up to 4,750 |
| r6gd.4xlarge | 16 | 128 | 1×950 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 | 4,750 |
| r6gd.8xlarge | 32 | 256 | 1×1900 NVMe SSD | 12 | 9,000 |
| r6gd.12xlarge | 48 | 384 | 2×1425 NVMe SSD | 20 | 13,500 |
| r6gd.16xlarge | 64 | 512 | 2×1900 NVMe SSD | 25 | 19,000 |
| r6gd.metal | 64 | 512 | 2×1900 NVMe SSD | 25 | 19,000 |
AWS initially offered the M6g instances in 8 sizes:
| Instance Name | vCPUs | Memory (GiB) | Price/Hour (Linux) | Price/Hour (RHEL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6g.medium | 1 | 4 | $0.0385 | $0.0985 |
| m6g.large | 2 | 8 | $0.0770 | $0.1370 |
| m6g.xlarge | 4 | 16 | $0.1540 | $0.2140 |
| m6g.2xlarge | 8 | 32 | $0.3080 | $0.4380 |
| m6g.4xlarge | 16 | 64 | $0.6160 | $0.7460 |
| m6g.8xlarge | 32 | 128 | $1.2320 | $1.3620 |
| m6g.12xlarge | 48 | 192 | $1.8480 | $1.9780 |
| m6g.16xlarge | 64 | 256 | $2.4640 | $2.5940 |
Considerations for Migrating Workloads to Amazon EC2 Graviton2 Instances
The new Graviton2 instances are supported by several open-source software distributions and services.
Here is the list of support for Graviton2 instances:
- Amazon Linux 2, Ubuntu 16.04, 18.04, and newer, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.6 and 8.0, SUSE, Fedora, Debian, FreeBSD, NetBSD, Amazon Corretto distribution of OpenJDK
- Docker Desktop, Amazon ECS, Amazon EKS for containers.
- Amazon CloudWatch, AWS Systems Manager, AWS CodeCommit, Cloud9, CodePipeline, and Amazon Inspector for tools
- Code Suite, Jenkins
Graviton2 now has better software ecosystem than the initial AWS Arm-based A1 instances and continues to make a great use of the AWS Nitro System, an AWS platform that abstracts the underlying hardware via a thin hypervisor.
Nitro has been around for years, but AWS has rearchitected its infrastructure based on it. The upshot is that AWS can move workloads to any architecture and processor.
AWS has noted that Nitro is how they are using virtualization and optimizing the stack across hardware and software, allowing the, to modularize and build new platforms easier. ASICs take functions off core hardware and are optimized for tasks. In a nutshell, Nitro is the hypervisor created for AWS and allows the cloud provider to swap out processors and architectures easily.
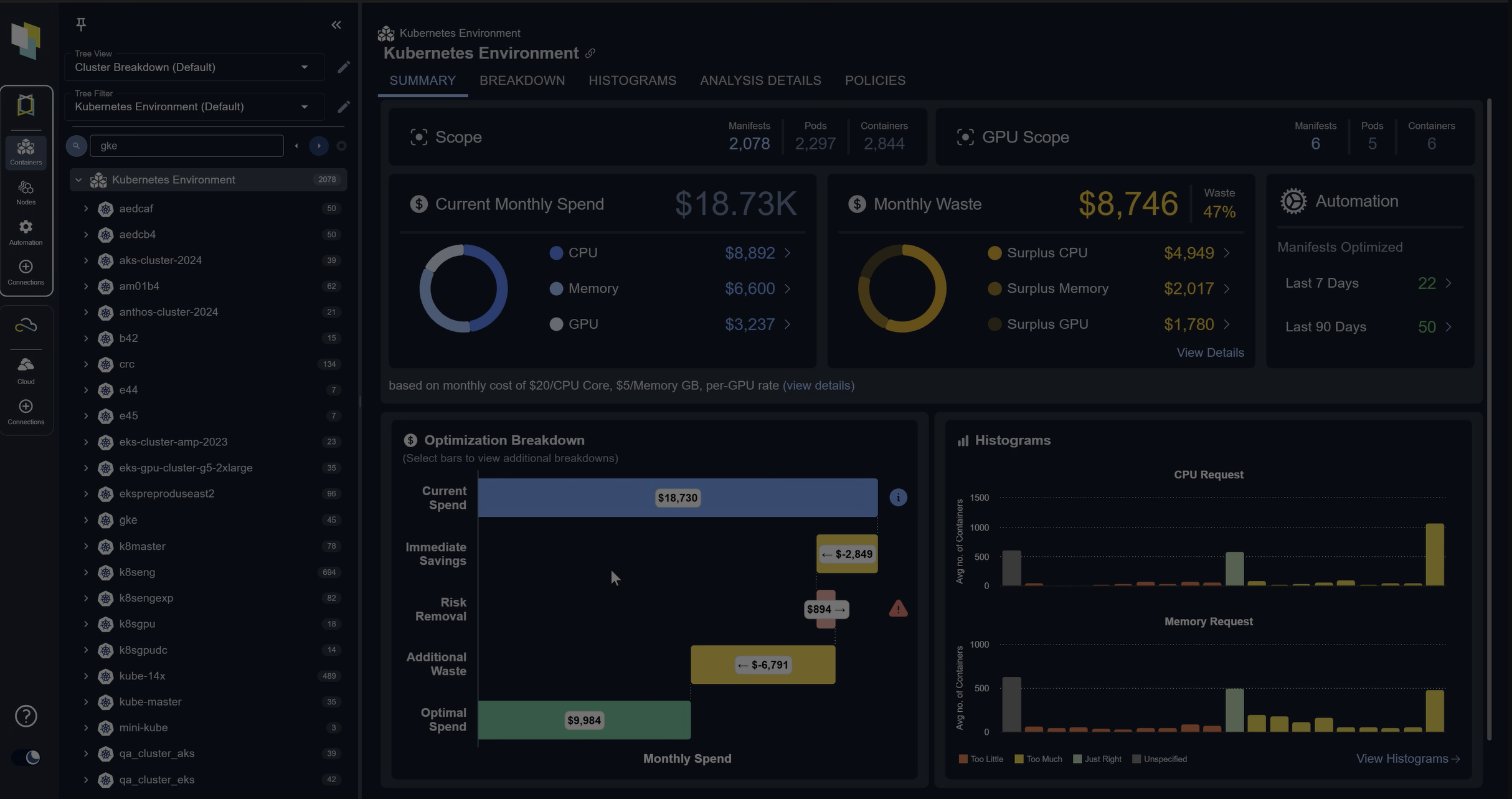
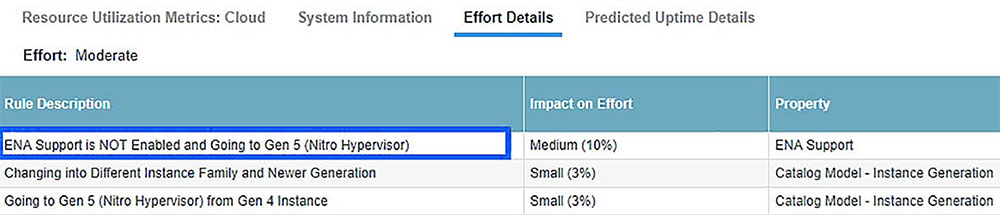
Densify performs comprehensive checks leveraging our patented, rule-driven engine to compare the requirements of your workloads against the capabilities of different cloud instance types based on metadata from AWS. We make sure only suitable workloads are considered as migration candidates for M6g, and any additional considerations are highlighted and presented to our users.
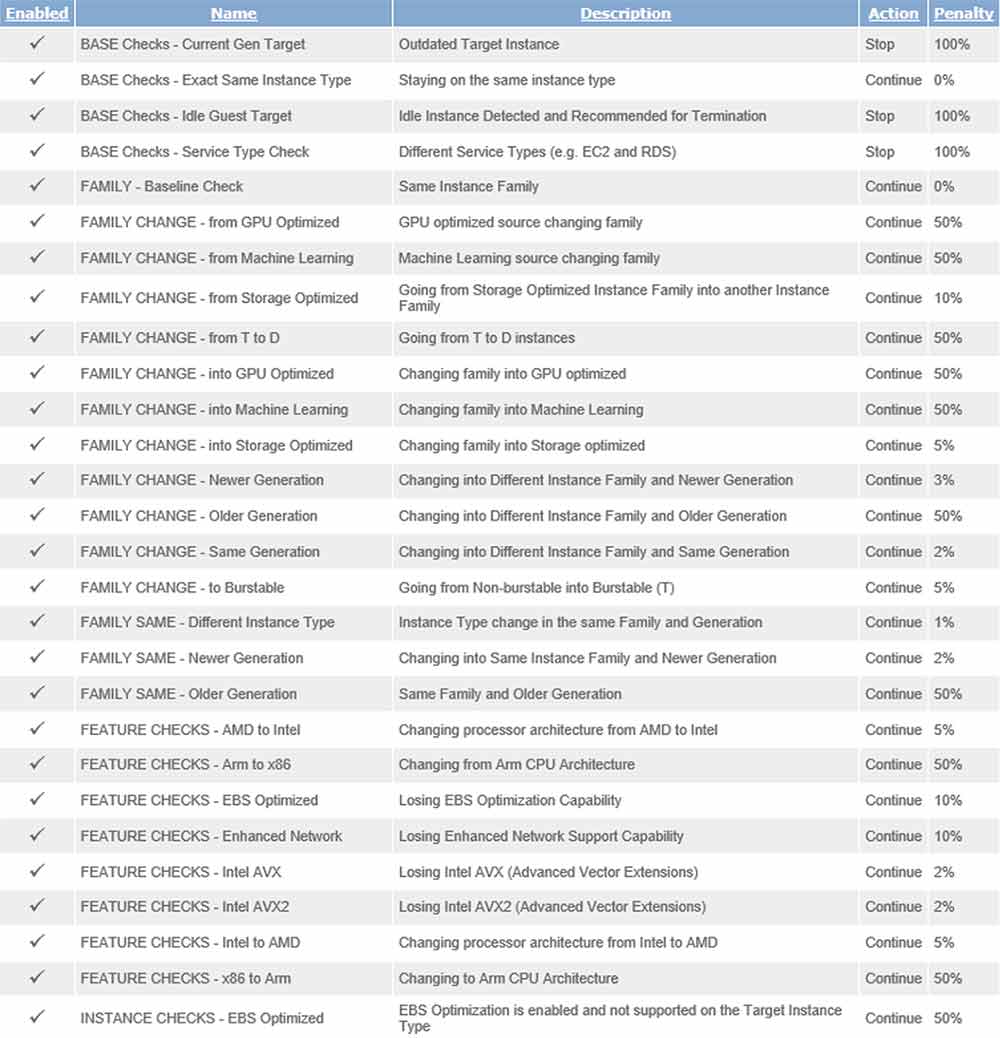
One of the workload analysis rules in action:
Cost Comparison of M6g vs T3, M5, C5, & R5 Instances
Let’s compare EC2 instances with 32 GB of RAM using US East (Northern Virginia) Region prices:
| Instance< Size | vCPUs | Baseline Performance per 1 vCPU | Memory (GiB) | Price/Hour (Linux) | Price/Hour (Windows) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M6g.2xlarge | 8 | n/a | 32 | $0.3080 | n/a |
| T3.2xlarge | 8 | 40% | 32 | $0.3328 | $0.4800 |
| M5.2xlarge | 8 | n/a | 32 | $0.3840 | $0.7520 |
| M5a.2xlarge | 8 | n/a | 32 | $0.3440 | $0.7120 |
| C5.4xlarge | 16 | n/a | 32 | $0.6800 | $1.4160 |
| R5.xlarge | 4 | n/a | 32 | $0.2520 | $0.4360 |
Assuming the following:
- Instances running @ 100% for a 1-month period
- Baseline performance for t3.2xlarge is 3.2 vCPUs (40% * 8 vCPUs)
- Additional charges of $0.05 (for Linux) and $0.096 (for Windows) per vCPU-hour for .6/*T3 bursting beyond credits
Here are the monthly costs for the various instance types:
| Instance Size | Linux | Windows |
|---|---|---|
| M6g.2xlarge | $221.76 | n/a |
| T3.2xlarge (throttled) | $239.62 | $325.60 |
| T3.2xlarge (unlimited) | $412.42 | $677.38 |
| M5.2xlarge | $276.48 | $541.44 |
| M5a.2xlarge | $247.68 | $512.64 |
| C5.4xlarge | $439.60 | $1019.52 |
| R5.xlarge | $181.44 | $313.92 |
Key Considerations for Running Workloads on AWS Graviton2 Arm Processors
- The Graviton2-based instances have no Windows compatibility today
- T3-based instances @100% will cost significantly more than the comparable M4 and R5 Instances
- The M6g.2xlarge was the cheapest option of the compared instances that had 8 vCPUs
- R5 is still the cheapest option to buy RAM but that probably only until R6g instances become available
Considerations for Reserved Instance & Savings Plans Purchases of Graviton2 Instances
With both Reserved Instances and Savings Plans available ,customers need to be aware of savings opportunities. With the help of Densify analytics and expert advice from our Cloud Advisors, you will be able to plan and execute comprehensive Reserved Instances and Savings Plans purchases along with Reserved Instances exchanges to increase your overall coverage and protect your existing investments.
Successfully Matching Candidate Workloads to Graviton2 Instances
Densify is the only technology with complete knowledge of available services and configurations across public cloud, private cloud, and container environments to deliver actionable and automatible optimization directives. Request a demo and see how we will deliver the most precise answer for where to place your apps and workloads in AWS.