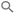Working with Virtual Machine Scale Sets
Working with Virtual Machine Scale Sets
#380920
Azure VM Scale Set (VM Scale Set) let you create and manage a group of load balanced VMs. The number of VM instances can be automatically increased or decreased in response to demand or on a defined schedule. Densify analyzes your VM Scale Sets and provides optimization recommendations.
When working with VM Scale Sets note the following:
- Virtual machine instances that belong to a scale set are logically considered to be part of the VM Scale Set service entity and recommendations are made for the group and not for the individual instances.
- VM Scale Sets configured with maximum group size = 1, are treated as VMs and are only included in the Virtual Machine tab, while VM Scale Sets configured with maximum group size > 1, are shown on the VM Scale Set tab.
- Densify cannot analyze VM Scale Sets configured with their orchestration mode = Flexible. However, a flexible scale configured to run on one instance type can be analyzed. See Working with Virtual Machine Scale Sets.
- Azure provides memory metrics during data collection. If for some reason, memory data is not available, the backfill memory settings will be used for the analysis. See VM Scale Set Backfilling Memory.
- The Impact Analysis and Recommendation Report report is not currently available for VM Scale Sets with maximum size >1. Also note the following feature support:
Table: Feature Support for VM Scale Set
|
Feature |
VM Scale Set with Max Size=1 |
VM Scale Set with Max Size>1 |
|
Impact Analysis and Recommendation Report for both UI and API |
Available in 2.4.0 |
Future Release |
|
Catalog Map |
Available in 2.4.0 |
Future Release |
|
Metrics Viewer |
Future Release |
Future Release |
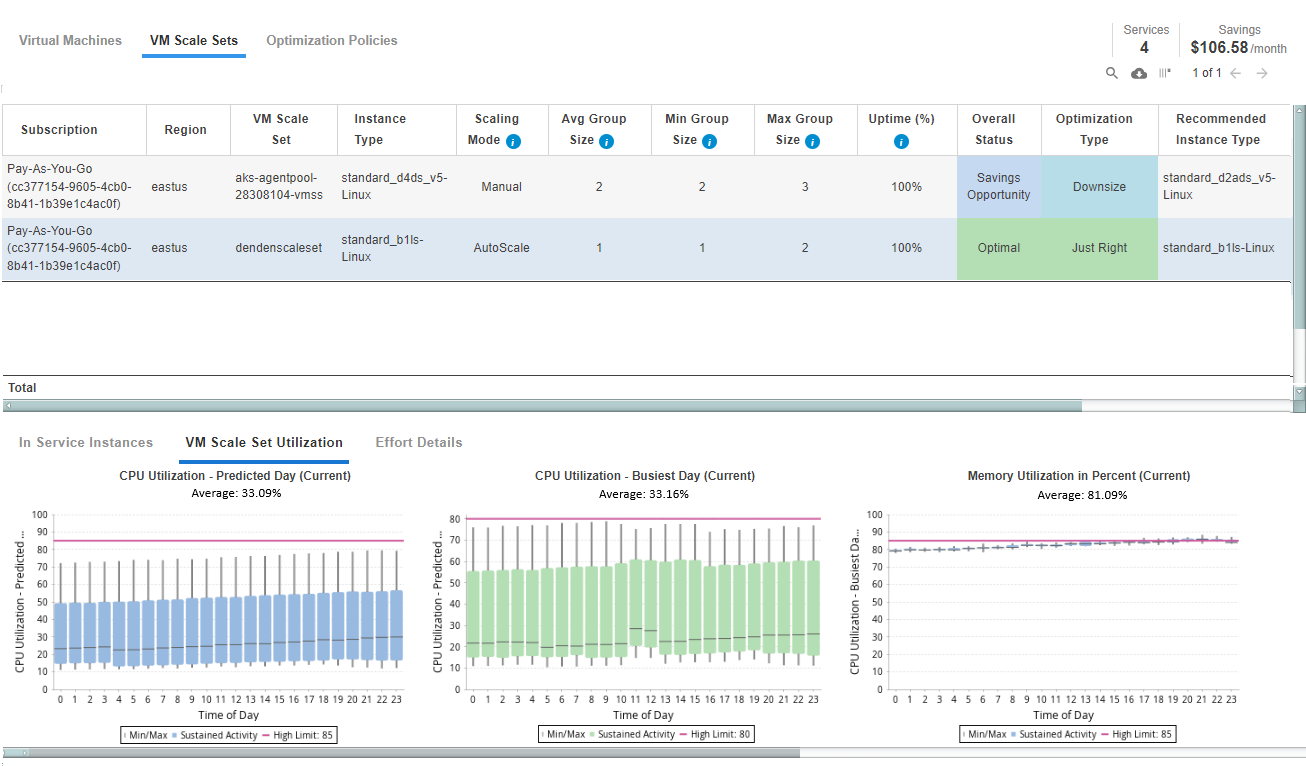
The VM Scale Setoptimization opportunity report is divided into two sections:
- The tabular report in the upper pane, shows details of each VM Scale Set and the recommendations.
- Tabs in the lower pane display the selected VM Scale Set's scaling activity and resource utilization details. A third tab shows the effort required to implement the recommendation.
The controls, in the upper right corner of the page, provide options for managing and viewing your data more effectively.
By default, the table is sorted by Efficiency Rating. This is still the case even if you select another Group By option. You can sort the content of this table using any of the available columns, by clicking the column header.
- Click the column header to sort the table, in ascending order, using the content of the selected table as the sort key.
- Click the column header again, to sort the table, in descending order, again using the content of the selected table as the sort key.
- Click the column header a third time to clear the sort and return to the default, sorted by Efficiency Rating.
An up/down arrow is displayed in the column header to indicate the column is being used to sort the content of the table.
Sorting is not persistent between pages or login sessions and this feature is only available on the Data tab.
VM Scale Set Tabular Report Sorting
The VM Scale Set tabular report is ordered based on the following sorting keys:
|
Sort Key |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
The VM Scale Sets are first sorted by Overall Status, in the following order:
|
|||
|
If the Overall Status is the same, then the secondary sort key is Optimization Type. services are sorted by Optimization Type in the following order:
|
|||
|
If Overall Status and Optimization Type are the same, then the tertiary sort key is the Account number, in ascending order. |
|||
|
If all of the above sort keys are the same, then the final sorting is done by the name, in ascending, alphabetical order. |
You can filter the optimization tabular report based on recommendations using the Recommendation Filter Menu. This filter allows you to narrow the results of your report based on overall status, optimization type, effort required and whether or not the recommendation should be deferred. For details, see
Densify cannot analyze VM Scale Set with a set of mixed instance types i.e. VM Scale Set configured with Orchestration Mode = Flexible. However, a scale set with Orchestration Mode = Flexible, can still be configured to run on one instance type and Densify can analyze these services.
Densify checks the VM Scale Set to determine if it is actually configured to run a mix of instance types or to run on a single instance type. Mixed groups are tagged by setting the attribute, "Mixed Instance Policy Set" to True and these scale sets are filtered from the analysis using the Cloud Environment filter.
Additionally, Densify detects mixed instance configurations that result from changes to the launch configuration/scale set model. When the configuration of a VM Scale Set changes then in the event of scale out, new instances are created based on the new configuration, while the existing child instances continue to run with the previous configuration.
In the event of a scale in, VM Scale Sets are typically set to favour terminating instances created via the old launch template. This behaviour may also result in a mix of instance types.
Densify detects these changes and excludes services where the configuration of the scale set has changed but the running child-instances have not been affected.
The tabular report displays the current and recommended instance sizing and cost details for each VM Scale Set.
Recommended group sizing associated with downscaling or upscaling the VM Scale Set are included. See the Working with Virtual Machine Scale Sets or the Working with Virtual Machine Scale Sets columns for the recommended sizing.
|
Column Name |
Description |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The Azure account containing the VM Scale Set. |
|||||||
|
Region |
The region containing the VM Scale Set. |
||||||
|
Availability Zone |
The availability zone containing the VM Scale Set. The AZ corresponds to a geographic region. This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
||||||
|
The VM Scale Set name, discovered during data collection. |
|||||||
| A unique key assigned by the public cloud vendors to identify this instance. This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
|||||||
|
This column indicates the name of the AKS cluster managing the VM Scale Set. The AKS cluster is obtained from the resource group's tags. i.e. "Resource Tags" attribute containing “aks-managed-cluster-name: <cluster name>". Note: This column is visible only if the VM Scale Set is hosting an AKS cluster. |
|||||||
|
This column indicates the name of the Kubernetes cluster that the VM Scale Set is hosting. When populated the analysis requires additional information to ensure the VM Scale Set can satisfy all of the container requests. If the column "K8s Node Group" is populated with a dash (-) or the column is not visible, then consider deploying the Densify data forwarder Note: This column is available only if the VM Scale Set is hosting a Kubernetes cluster. |
|||||||
|
This column indicates the name of the Kubernetes cluster name as configured in the Densify data forwarder.
This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
|||||||
|
This column indicates the name of the Kubernetes node group associated with this VM Scale Set. When populated, Densify has the data required for enhanced Scale Group analysis. Note: This column is available only if the VM Scale Set is hosting a Kubernetes cluster.
This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
|||||||
|
Instance Type |
The current catalog instance is listed. This value is based on the data collected. |
||||||
|
Scaling Mode |
The scaling mode applied to this VM Scale Set. The scaling mode can be one of manual or autoscale. If the VM Scale Set is currently running in manual mode, consider changing it to autoscale mode. The proposed recommended instance type, minimum and maximum group size are based on scaling mode being set to autoscale. |
||||||
|
No. of Profiles |
The number of profiles associated with the selected VM Scale Set. Profiles are only applicable to scale sets with scaling mode=Autoscale. By default, scale sets with orchestration mode=Uniform are created with one scaling profile. Multiple profiles can be used to scale in different ways at different times. If for example, your workloads are inactive on some weekends, a recurring profile to scale in resources can be applied. |
||||||
|
Orchestration Mode |
The orchestration mode applied to this VM Scale Set. The orchestration mode can be one of Uniform or Flexible. Only Uniform scale sets, or Flexible scale sets running identical instance types are analyzed. See Mixed Mode Services for details. The proposed recommended instance type, minimum and maximum group size are based on the orchestration mode being set to uniform. |
||||||
|
Avg Group Size |
The average instance count when the VM Scale Set is running. |
||||||
|
The minimum number of instances/hour. When configured to autoscale, this value is the minimum of all the profiles associated with the selected VM Scale Set. When configured to scale manually, this is the minimum number of instances found during the historical period that is used for the analysis. The historical period is defined by the policy setting, "Workload range". |
|||||||
|
This is the maximum number of instances/hour. When configured to autoscale this value is the maximum of all the profiles associated with the selected VM Scale Set. When configured to scale manually, this is the maximum number of instances found during the historical period that is used for the analysis. The historical period is defined by the policy setting, "Workload range". |
|||||||
|
Uptime (%) |
The Predicted_uptime%, and not the observed uptime percent. When using pay-per-use pricing models, the amount of time each instance has been running, is required to accurately estimate future costs. The predicted uptime (%) for a cloud instance or container, is based on the percentage of hours CPU utilization data is present in the historical interval, as specified in the policy settings for the entity. For Auto Scaling groups and VM Scale Sets and Individual child instances are not taken into account. Predicted uptime %, for new instances or containers, that started mid-way through the historical interval, is calculated from the time/date that the instance was started as opposed to the beginning of the interval, resulting in more accurate predictions for future usage. For example, the uptime is the number of hours that have "CPU Utilization in mcores", and the range is the lesser of when the container was discovered, or the range defined in the policy. Looking at a specific container that was discovered on Jan 5th 2024, that has workload of 42 hours since that date, then the uptime % is 42 hrs/(13 days x 24 hrs/day) = 13.4%. This is the value shown in this column. |
||||||
|
Total Hrs |
The total number of hours since the VM Scale Set was created. This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
||||||
|
Running Hrs |
The number of hours that the VM Scale Set has been running. Both Total Hrs and Running Hrs are restricted by the historical time range defined in the policy (i.e. 60d history). This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
||||||
|
Identifies the overall status of the optimization results based on Optimization Type and potential Net Savings ($/Month)
|
|||||||
|
The recommended action for the group of instances. See |
|||||||
|
Recommended Instance Type |
This is the recommended catalog instance, based on optimization analysis. |
||||||
|
The predicted average instance count on the recommended instance type. |
|||||||
|
Recom. Min Group Size |
The minimum number of instances recommended for the scale group. |
||||||
|
Recom. Max Group Size |
The maximum number of instances recommended for the scale group. |
||||||
|
This value indicates whether the scaling mode needs to be reviewed. Possible values depend on whether or not the VM Scale Set is managed by AKS:
|
|||||||
|
The estimated cost savings per month. The predicted average instance counts, the instance type cost and predicted uptime are used to calculate the current and recommended estimated cost. The savings are calculated as the current estimated cost minus the recommended estimated cost. |
|||||||
|
[ High | Medium | Low | None ] This column describes the effort required to investigate and implement the Densify recommendations. The displayed group effort is an average of all the calculated efforts for each instance (or service) in the group. Effort for each instance is calculated by rule-driven analytics based on factors (such as family change, storage change, data quality checks, feature changes, etc.) that can be configured in the policy settings and rule set which captures best practices. See the Effort Details tab in the lower pane for additional effort details for the selected VM Scale Set. There will be an impact to the effort value for VM Scale Sets, hosting a Kubernetes cluster that not linked with a AKS reference (i.e. has no parent identified). |
|||||||
|
Current CPU |
The CPU allocation for the current instance type. This value is for a single instance and is not multiplied by the average number of instances. This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
||||||
|
Recommended CPU |
The CPU allocation for the recommended instance type. This value is for a single instance and is not multiplied by the average number of instances. This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
||||||
|
Current CPU Benchmark |
The CPU benchmark value for the current instance type. This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
||||||
|
Recommended CPU Benchmark |
The CPU benchmark value for the recommended instance type. This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
||||||
|
Current Memory Allocation (GB) |
The memory allocation for the current instance type. This value is for a single instance and is not mulitplied by the average number of instances. This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
||||||
|
Recommended Memory Allocation (GB) |
The memory allocation for the recommended instance type. This value is for a single instance and is not mulitplied by the average number of instances. This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
||||||
|
Instance Type Updated On |
A value in this column indicates the instance type has been changed recently. The workload for this instance, on which the recommendation is based, includes only the days of data from the indicated date to the current date. All historical data for this instance, collected prior to the indicated date is not included in the analysis. Previous data has been excluded because it was based on the previous instance type. A blank cell indicates the current instance type has not changed and all available workload data within the range, defined by the policy, has been used to generate the recommendation. Contact [email protected] to enable this feature. See Relearning Workload Patterns for more details. This column is hidden by default. You can enable it for display, as required. See Data Controls, above. |
||||||
|
Total Savings ($/Month) |
Total savings based on making all of the recommended changes. This is the sum of all net monthly savings. If the number of VM Scale Sets spans multiple pages this is the total for all pages. |
Reviewing Specific Instance Details
The bottom pane of the VM Scale Set report provides the following information for the row, selected in the tabular report:
- In Service Instances—Shows workload charts for current and recommended predicted scaling activities for the selected VM Scale Set. For VM Scale Sets identified with optimization type="Just Right" or "Terminate", only the current in-service scaling activity chart is displayed.
- VM Scale Set Utilization —Shows charts for current and recommended CPU Utilization and Memory Utilization for the selected VM Scale Set. Network I/O, Disk I/O workload charts are also included, showing utilization at the VM Scale Set level. You can view workload charts for each group member from the Working with Virtual Machine Scale Sets page.
- Effort Details Tab—This table lists the factors that contribute to the effort required to investigate and implement the Densify recommendations. Effort for each group is calculated by rule-driven analytics based on factors (such as instance family change, data quality checks, feature changes, etc.) that can be configured in the policy settings and through analysis rule sets. A description of each rule is provided.
VM Scale Set Optimization Report Details
Exporting the VM Scale Set Optimization Opportunity Report
- Click the download CSV icon to export the content of the VM Scale Set dashboard to a .CSV file.
- Locate and open your download folder to see your exported data.
The VM Scale Set Summary report contains the tabular list of VM Scale Sets from the optimization opportunity tabular list view. All selected filtering options are applied to the exported data
Additional Considerations for VM Scale Set Recommendations
AKS-aware VM Scale Set Recommendations
VM Scale Sets and their virtual machine group members are loaded from Azure cloud data collection audits and Kubernetes entities are collected via the Densify data forwarder from Prometheus data. Linking these entities is extremely complex.
A single Kubernetes cluster can run on one or more VM Scale Set with each VM Scale Set running in a node group within the cluster; however it is possible to skip node groups, and in this case the VM Scale Set must be linked directly to the cluster entity.
Densify uses the parent resource group and its tags to match the entities and VM Scale Set recommendations are made based on the established AKS-VM Scale Set associations.
VM Scale Set Backfilling Memory
Memory metrics are available for Azure instances when using the standard Densify audit. If, for some reason, you are not collecting memory metrics, Densify provides a method to simulate memory utilization using backfill memory policy settings. Contact [email protected] for details.